Are you or a loved one dealing with a gambling problem? Explore the warning signs and symptoms and learn how to stop.
- 10 Signs Of Gambling Addiction
- How To Beat Gambling Addiction
- How To Beat Gambling Addiction On Your Own
- Solutions To Gambling Addiction
- Gambling Addiction Treatment
What is gambling addiction and problem gambling?
Gambling problems can happen to anyone from any walk of life. Your gambling goes from a fun, harmless diversion to an unhealthy obsession with serious consequences. Whether you bet on sports, scratch cards, roulette, poker, or slots—in a casino, at the track, or online—a gambling problem can strain your relationships, interfere with work, and lead to financial disaster. You may even do things you never thought you would, like running up huge debts or even stealing money to gamble.
See full list on mayoclinic.org. Gambling can be a fun once-in-a-while activity or, for the lucky few, a way to win that illusive jackpot. Unfortunately, gamblers can become obsessive and compulsive about playing the ponies or pulling the one-armed bandit. They may find themselves in the throes of an addiction that could ruin them financially, socially, psychologically or even physically.
Gambling addiction—also known as pathological gambling, compulsive gambling or gambling disorder—is an impulse-control disorder. If you’re a compulsive gambler, you can’t control the impulse to gamble, even when it has negative consequences for you or your loved ones. You’ll gamble whether you’re up or down, broke or flush, and you’ll keep gambling regardless of the consequences—even when you know that the odds are against you or you can’t afford to lose.
Of course, you can also have a gambling problem without being totally out of control. Problem gambling is any gambling behavior that disrupts your life. If you’re preoccupied with gambling, spending more and more time and money on it, chasing losses, or gambling despite serious consequences in your life, you have a gambling problem.
A gambling addiction or problem is often associated with other behavior or mood disorders. Many problem gamblers also suffer with substance abuse issues, unmanaged ADHD, stress, depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder. To overcome your gambling problems, you’ll also need to address these and any other underlying causes as well.
Although it may feel like you’re powerless to stop gambling, there are plenty of things you can do to overcome the problem, repair your relationships and finances, and finally regain control of your life.
The first step is to separate the myths from the facts about gambling problems:
| Myths and Facts about Gambling Problems |
Myth: You have to gamble every day to be a problem gambler. Fact: A problem gambler may gamble frequently or infrequently. Gambling is a problem if it causes problems. |
Myth: Problem gambling is not really a problem if the gambler can afford it. Fact: Problems caused by excessive gambling are not just financial. Too much time spent on gambling can also lead to relationship and legal problems, job loss, mental health problems including depression and anxiety, and even suicide. |
Myth: Having a gambling problem is just a case of being weak-willed, irresponsible, or unintelligent. Fact: Gambling problems affect people of all levels of intelligence and all backgrounds. Previously responsible and strong-willed people are just as likely to develop a gambling problem as anyone else. |
Myth: Partners of problem gamblers often drive their loved ones to gamble. Fact: Problem gamblers often try to rationalize their behavior. Blaming others is one way to avoid taking responsibility for their actions, including what is needed to overcome the problem. |
Myth: If a problem gambler builds up a debt, you should help them take care of it. Fact: Quick fix solutions may appear to be the right thing to do. However, bailing the gambler out of debt may actually make matters worse by enabling their gambling problems to continue. |
Gambling addiction signs and symptoms
Gambling addiction is sometimes referred to as a “hidden illness” because there are no obvious physical signs or symptoms like there are in drug or alcohol addiction. Problem gamblers also typically deny or minimize the problem—even to themselves. However, you may have a gambling problem if you:
Feel the need to be secretive about your gambling. You might gamble in secret or lie about how much you gamble, feeling others won’t understand or that you will surprise them with a big win.
Have trouble controlling your gambling. Once you start gambling, can you walk away? Or are you compelled to gamble until you’ve spent your last dollar, upping your bets in a bid to win lost money back?
Gamble even when you don’t have the money. You may gamble until you’ve spent your last dollar, and then move on to money you don’t have—money to pay bills, credit cards, or things for your children. You may feel pushed to borrow, sell, or even steal things for gambling money.
Have family and friends worried about you. Denial keeps problem gambling going. If friends and family are worried, listen to them carefully. It’s not a sign of weakness to ask for help. Many older gamblers are reluctant to reach out to their adult children if they’ve gambled away their inheritance, but it’s never too late to make changes for the better.
Self-help for gambling problems
The biggest step to overcoming a gambling addiction is realizing that you have a problem. It takes tremendous strength and courage to own up to this, especially if you have lost a lot of money and strained or broken relationships along the way. Don’t despair, and don’t try to go it alone. Many others have been in your shoes and have been able to break the habit and rebuild their lives. You can, too.
Learn to relieve unpleasant feelings in healthier ways. Do you gamble when you’re lonely or bored? Or after a stressful day at work or following an argument with your spouse? Gambling may be a way to self-soothe unpleasant emotions, unwind, or socialize. But there are healthier and more effective ways of managing your moods and relieving boredom, such as exercising, spending time with friends who don’t gamble, taking up new hobbies, or practicing relaxation techniques.
Strengthen your support network. It’s tough to battle any addiction without support, so reach out to friends and family. If your support network is limited, there are ways to make new friends without relying on visiting casinos or gambling online. Try reaching out to colleagues at work, joining a sports team or book club, enrolling in an education class, or volunteering for a good cause.
Join a peer support group. Gamblers Anonymous, for example, is a 12-step recovery program patterned after Alcoholics Anonymous. A key part of the program is finding a sponsor, a former gambler who has experience remaining free from addiction and can provide you invaluable guidance and support.
Seek help for underlying mood disorders.Depression, stress, substance abuse, or anxiety can both trigger gambling problems and be made worse by compulsive gambling. Even when gambling is no longer a part of your life, these problems will still remain, so it’s important to address them.
How to stop gambling for good
For many problem gamblers, it’s not quitting gambling that’s the biggest challenge, but rather staying in recovery—making a permanent commitment to stay away from gambling. The Internet has made gambling far more accessible and, therefore, harder for recovering addicts to avoid relapse. Online casinos and bookmakers are open all day, every day for anyone with a smartphone or access to a computer. But maintaining recovery from gambling addiction or problem gambling is still possible if you surround yourself with people to whom you’re accountable, avoid tempting environments and websites, give up control of your finances (at least at first), and find healthier activities to replace gambling in your life.
10 Signs Of Gambling Addiction
Making healthier choices
One way to stop gambling is to remove the elements necessary for gambling to occur in your life and replace them with healthier choices. The four elements needed for gambling to continue are:
A decision: For gambling to happen, you need to make the decision to gamble. If you have an urge: stop what you are doing and call someone, think about the consequences to your actions, tell yourself to stop thinking about gambling, and find something else to do immediately.
Money: Gambling cannot occur without money. Get rid of your credit cards, let someone else be in charge of your money, have the bank make automatic payments for you, close online betting accounts, and keep only a limited amount of cash on you.
Time: Even online gambling cannot occur if you don’t have the time. Schedule enjoyable recreational time for yourself that has nothing to do with gambling. If you’re gambling on your smartphone, find other ways to fill the quiet moments during your day.
A game: Without a game or activity to bet on there is no opportunity to gamble. Don’t put yourself in tempting environments. Tell gambling establishments you frequent that you have a gambling problem and ask them to restrict you from entering. Remove gambling apps and block gambling sites on your smartphone and computer.
Finding alternatives to gambling
Maintaining recovery from gambling addiction depends a lot on finding alternative behaviors you can substitute for gambling. Some examples include:
| Reason for gambling | Sample substitute behaviors |
| To provide excitement, get a rush of adrenaline | Sport or a challenging hobby, such as mountain biking, rock climbing, or Go Kart racing |
| To be more social, overcome shyness or isolation | Counseling, enroll in a public speaking class, join a social group, connect with family and friends, volunteer, find new friends |
| To numb unpleasant feelings, not think about problems | Try therapy or use HelpGuide’s free Emotional Intelligence toolkit |
| Boredom or loneliness | Find something you’re passionate about such as art, music, sports, or books and then find others with the same interests |
| To relax after a stressful day | As little as 15 minutes of daily exercise can relieve stress. Or deep breathing, meditation, or massage |
| To solve money problems | The odds are always stacked against you so it’s far better to seek help with debts from a credit counselor |
Dealing with gambling cravings
Feeling the urge to gamble is normal, but as you build healthier choices and a strong support network, resisting cravings will become easier. When a gambling craving strikes:
Avoid isolation. Call a trusted family member, meet a friend for coffee, or go to a Gamblers Anonymous meeting.
Postpone gambling. Tell yourself that you’ll wait 5 minutes, fifteen minutes, or an hour. As you wait, the urge to gamble may pass or become weak enough to resist.
Visualize what will happen if you give in to the urge to gamble. Think about how you’ll feel after all your money is gone and you’ve disappointed yourself and your family again.
Distract yourself with another activity, such as going to the gym, watching a movie, or practicing a relaxation exercise for gambling cravings.
Coping with lapses
If you aren’t able to resist the gambling craving, don’t be too hard on yourself or use it as an excuse to give up. Overcoming a gambling addiction is a tough process. You may slip from time to time; the important thing is to learn from your mistakes and continue working towards recovery.
Gambling addiction treatment
Overcoming a gambling problem is never easy and seeking professional treatment doesn’t mean that you’re weak in some way or can’t handle your problems. But it’s important to remember that every gambler is unique so you need a recovery program tailored specifically to your needs and situation. Talk to your doctor or mental health professional about different treatment options, including:
Inpatient or residential treatment and rehab programs. These are aimed at those with severe gambling addiction who are unable to avoid gambling without round-the-clock support.
Treatment for underlying conditions contributing to your compulsive gambling, including substance abuse or mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, OCD, or ADHD. This could include therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Problem gambling can sometimes be a symptom of bipolar disorder, so your doctor or therapist may need to rule this out before making a diagnosis.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy. CBT for gambling addiction focuses on changing unhealthy gambling behaviors and thoughts, such as rationalizations and false beliefs. It can also teach you how to fight gambling urges and solve financial, work, and relationship problems caused by problem gambling. Therapy can provide you with the tools for coping with your addiction that will last a lifetime.
Family therapy and marriage, career, and credit counseling. These can help you work through the specific issues that have been created by your problem gambling and lay the foundation for repairing your relationships and finances.
How to help someone stop gambling
If your loved one has a gambling problem, you likely have many conflicting emotions. You may have spent a lot of time and energy trying to keep your loved one from gambling or having to cover for them. At the same time, you might be furious at your loved one for gambling again and tired of trying to keep up the charade. Your loved one may have borrowed or even stolen money with no way to pay it back. They may have sold family possessions or run up huge debts on joint credit cards.
How To Beat Gambling Addiction
While compulsive and problem gamblers need the support of their family and friends to help them in their struggle to stop gambling, the decision to quit has to be theirs. As much as you may want to, and as hard as it is seeing the effects, you cannot make someone stop gambling. However, you can encourage them to seek help, support them in their efforts, protect yourself, and take any talk of suicide seriously.
Preventing suicide in problem gamblers
When faced with the consequences of their actions, problem gamblers can suffer a crushing drop in self-esteem. This is one reason why there is a high rate of suicide among compulsive gamblers. If you suspect your loved one is feeling suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-8255 or visit Befrienders Worldwide to find a suicide helpline in your country.
Four tips for family members:
- Start by helping yourself. You have a right to protect yourself emotionally and financially. Don’t blame yourself for the gambler’s problems or let his or her addiction dominate your life. Ignoring your own needs can be a recipe for burnout.
- Don’t go it alone. It can feel so overwhelming coping with a loved one’s gambling addiction that it may seem easier to rationalize their requests “this one last time.” Or you might feel ashamed, feeling like you are the only one who has problems like this. Reaching out for support will make you realize that many families have struggled with this problem.
- Set boundaries in managing money. To ensure the gambler stays accountable and to prevent relapse, consider taking over the family finances. However, this does not mean you are responsible for micromanaging the problem gambler’s impulses to gamble. Your first responsibilities are to ensure that your own finances and credit are not at risk.
- Consider how you will handle requests for money. Problem gamblers often become very good at asking for money, either directly or indirectly. They may use pleading, manipulation, or even threats to get it. It takes practice to ensure you are not enabling your loved one’s gambling addiction.
| Do’s and Don’ts for Partners of Problem Gamblers |
| Do… |
|
| Don’t… |
|
Annual profits for the gambling industry in the United States are around $40 billion.
For those who fill an emotional need or seek euphoria through gambling, a lot of help is necessary to overcome the driving need to gamble.
Helping a true gambling addict to recognize they have a severe problem is the first step towards gambling addiction recovery, but they will need ongoing support to make it to the other side.
Through it all, continue to be patient and encouraging while always maintaining a non-judgmental attitude.
That will help no matter which ways you find work the best for helping a loved one to recover from an addition to gambling.
Contents
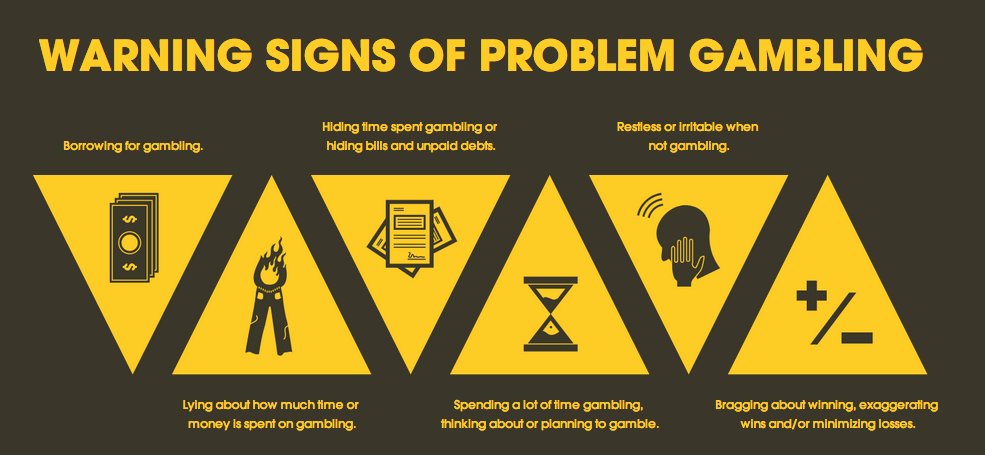
1. Identify signs of the problem
The first step is to look for many signs that come with compulsive gambling, which is where the issue occurs.
Lying, theft or other illegal activities, as well as a constant need to increase the stakes are signs of compulsive gambling and a serious problem.
Hiding the extent of their gambling habit or how much money is involved are also key signs that the problem needs to be addressed now.
2. Don’t judge
Prepare for a defensive reaction and be clear that the concern you have is not about judging their behavior.
Use “I” statements and ask if other parts of their life seem to be in need of attention.
Above all, make sure to let them know that you care – repeatedly.
3. Learn the difference between problem gambling and addiction
Problem gambling is behavior that disrupts your life.
Addiction means gambling is uncontrollable for you.
You are suffering from an impulse control disorder.
This means that no matter how much money you have, how it will affect loved ones and whether you are currently winning or losing, you keep gambling.
4. Understand the causes, contributing factors and personality traits related to gambling
Causes for gambling can range from a stressful day and a desire for a distraction to the need for a rush or a means of social interaction.
Knowing the main reason that a gambler turns to the habit can make it easier to find substitute behaviors to suggest and help the gambler utilize instead of gambling.
5. Research treatment
There are different avenues of treatment for gambling.
It is possible to work on treating the habit and problems at home.
Seeing a therapist in the company of the family can be helpful in an effort to resolve issues with gambling.
There are treatment centers that have programs for those who can’t stop themselves from gambling.
Typically, gambling occurs with an underlying condition, and the underlying conditions being treated can help with the gambling as well.
Finally, there is Cognitive Behavior Therapy or treatments with medication that can be recommended and managed by professionals for those who might benefit from these treatments.
6. Learn which treatment methods are more effective with different people and why
Medication can be helpful for treating underlying conditions like depression anxiety or ADHD.
CBT or therapy with the family can be helpful for those with social anxiety, the desire to interact in a healthy manner with others or those dealing with significant amounts of stress.
Each person has a different set of triggers and related factors for their gambling problem.
Different therapies can be effective once the causes are narrowed down.

7. Prepare for a negative reaction
Gamblers do not like to admit they have a problem.
Since that admission is so difficult, they are not going to want to stop gambling, much less seek treatment.
It is best to be prepared for their negativity and even the anger they may direct at you.
8. Talk to them about the issue
For those who are close to the gambler, an honest conversation is a must.
This will be difficult, but with preparation and a straight-forward, caring approach it can be done.
For those who are not close to the individual, the conversation should be with someone who is close to them.
9. Explain the probable consequences
Let the gambler know that there are some big potential issues that can arise if they continue feeding their habit.
Running out of money, legal issues and losing family due to the addiction are all key factors to mention.
It is also a good idea to remind them that gambling can be fun, but there comes a time when the fun has changed to serious addiction and problematic behavior.
10. Discuss treatment options with the gambler
Talk to the gambler about the possible causes for their gambling addiction.
Treatment options can start out with things like therapy and work toward inpatient programs or other methods if initial efforts fail.
For those who know that they have a serious problem and won’t be able to get past it on their own, then inpatient treatment and complete isolation from venues and gambling opportunities is the best option.
Talking to the gambler may provide some insight that can not be gained otherwise.
This makes it easier to address the problem and encourages their cooperation because they were consulted and feel their opinion is valued regarding their own shortcomings.
11. Encourage them to get help from a professional
With gambling, it is important to work with a professional.
This is particularly important because it allows an outside professional to determine the underlying causes and what treatments are required.
A professional is also objective, which is very important in situations of addiction, which causes very strong emotional reactions from loved ones.
The professional can provide the most accurate analysis of the situation, why the gambling is such a problem and how best to address the addiction and be able to move past it.
12. Use honesty to encourage honesty
Modeling is important for adults as well as children.
This is an important factor when considering a key factor in gambling situations, which is a lack of honesty.
It is important for people in a gambler’s life to be honest, even when they have bad days or backslide.
This encourages the gambler to be honest and let people know when they are struggling with the desire to gamble.
13. Address the issue of the debt associated with the problem
Gambling means money disappears fast.
Sadly, no one who gambles tends to get on a winning streak and stay on it.
Therefore, it is important to make the gambler very aware of what the addiction costs the family, any loved ones close to the gambler and the gambler themselves.
Money can be a huge incentive to quit gambling, because it is a finite resource.
It does not replenish itself, so the bank account doesn’t magically grow when no one is looking.
14. Be supportive during their treatment
Gambling can be a challenging problem to overcome.
As with any addiction, it is usually a big part of the gambler’s life and takes up a lot of their time.
When it comes time to address the problem and change the behavior, it is easier to do when others are there to help distract and refocus the gambler.
It is also not helpful when loved ones are judgmental and negative toward the gambler, as that tends to increase the chances of a relapse.
Those who overcome addiction successfully do so with an active support system, understanding family members and determination on the part of the gambler and those around him or her to push through and succeed no matter what.
15. Help them avoid situations where gambling is popular
Encourage the gambler to find other places to spend their time.
It is key to help them avoid the gambling venues they frequented in whatever manner necessary.
If they have a bad habit of stopping in just to see what’s going on, help them choose routes that do not go near the gambling venue when traveling to pay bills or complete other tasks.
16. Discuss the option of medication
Medication can be helpful to those with a gambling addiction.
Their addiction may be tied to compulsive behaviors due to a mental illness.
This mental illness may not be controllable through behavior modification or effort on the part of the gambler.
This is where medication can come into play.
When the underlying conditions are controlled with medication, then the gambling problem can be the sole focus and gain better results.
17. Encourage the gambler to attend a support group
For some, gambling is a way to have social interaction.
Regardless of whether that is a factor in a gambling habit, however, the decision to join a support group provides understanding, positive interactions and a way to spend time that keeps the gambler away from gambling venues.
Let the gambler know that joining a support group can be a beneficial way to take giant steps forward in the effort to overcome addiction.
18. Be prepared for the gambler to rationalize and excuse the habit
Gamblers spend a lot of time telling themselves their behavior is acceptable.
When confronted about the consequences and seriousness of their behavior, they are likely to try to give you the same reasons they tell themselves it is fine.
It is common to hear that gambling is not a problem if the gambler can afford the losses.
This may or may not be true, but it is a clear example of the fact that many people are more than willing to give reasons that gambling is an acceptable way to spend one’s time.
19. Understand relapse and why it may happen
In the case of an impulse control disorder like compulsive gambling, it is more than making a choice to change the habit.
It is also a lot of hard work, which means the process is a struggle.
Relapse is a common part of the process of overcoming addiction.
While it is not optimal for the gambler’s success, it should not be taken as a sign of ultimate failure either.
20. Watch for secretive behavior that may indicate relapse
Lying or leaving with no explanation are good indications that gamblers are relapsing.
Be suspicious of excuses for extended solo trips out of the house.
Frequent and lengthy “shopping trips” where nothing is purchased is a sign that something else may be going on.
21. Stay involved in their life to encourage them to overcome the habit
Gamblers are more likely to backslide when the loved ones in their life aren’t around during the day.
In order to encourage the success of the gambler in overcoming the addiction, it is best to keep in touch and make sure they are engaging in better decision making.
Let them know you are proud of their progress and encourage them after a backsliding incident to start fresh and try harder.
22. Encourage healthy choices to help avoid gambling
Physical activity, mindfulness and meditation and various hobbies that increase social interaction are all healthy ways to spend time.
Decisions, time and environment are all key factors to being healthy and avoiding temptation.
Choose to make better decisions that don’t involve gambling.
Schedule your time so you don’t have the opportunity to go gamble.
Finally, encourage the gambler to stay away from locations where temptations surround them. Remind them that if they can’t see a game or other activity to gamble on, it is harder to gamble.
23. Manage gambler’s finances to remove ability and therefore curb temptation
Taking control of the finances helps ensure the gambler does not have easy access to funds to spend on their addiction.
This keeps things on track when they do have an incident of backsliding.
Knowing when the money is spent and how much means it is addressed faster and efforts are made to avoid letting it happen again.
24. Introduce distractions and healthy hobbies to help gambler avoid the addiction
How To Beat Gambling Addiction On Your Own
Physical activities like hiking, mountain biking and rock climbing can be helpful hobbies to introduce to someone struggling with gambling.
The physical activity can be helpful as a distraction and also a new hobby allows them to narrow their focus to a new subject.
Counseling, a class like public speaking or volunteering at a worthwhile cause can be helpful because they connect the gambler to others in a positive social manner.
Solutions To Gambling Addiction
Meditation, deep breathing and hobbies that involve reading, music or art are all worthwhile considerations for new hobbies for the gambler as well.
Gambling Addiction Treatment
25. Keep the problem in the open and make others aware to help address the habit
Hiding the fact that someone in the family has a gambling problem can cause misunderstandings with other loved ones.
Make everyone aware that there is a gambling problem.
Keep communication open with other family members and let them know how they can help the person with the gambling problem overcome their addiction.